
In this article, you will have a clear understanding of how to use oauth2 authentication to implement facebook login with node js. Adding social login to your application has a lot of advantages. First of all, users of your application don't need to fill up a long registration form containing 10 or even more input fields.
Also while attempting to login to any application, they often forget their password. They, don't want to go through the password recovery process, as they find it tedious to do so.
The solution to this problem is if are able to register and login users to our application with their social network accounts in which they already have accounts. We can implement this functionality with the help of an authentication scheme known as Oauth2.
You can check out my article on the callback function here.
What is Oauth2
As per the official site of Oauth: OAuth 2.0 is the industry-standard protocol for authorization. OAuth 2.0 supersedes the work done on the original OAuth protocol created in 2006. OAuth 2.0 focuses on client developer simplicity while providing specific authorization flows for web applications, desktop applications, mobile phones, and living room devices.
In simple words, it is an authentication and authorization scheme in which users on the internet are able to access their information on other websites, without providing their account credentials ( username and/or password).
Only one requirement exists; that is, the user must authorize the application to access their data for a selected OAuth provider.
Why OAuth2 is Used
Users don't need to remember their credentials
Users can sign up or log in to any application that are using OAuth2 without using any credentials such as email id and/or password. They simply need to authorize the application to access their information for a selected OAuth provider. This step is done for one-time only.
Prevents security holes
In the Oauth2 mechanism, the user doesn't provide passwords to sign in or sign up for the application. So, from the development point of view, developers don't need to store a user's password. This, in fact, prevents inappropriate use of storing passwords.
Developer friendly
Developers can easily implement oauth2 in an application. They just need to go through the technical documentation for the specific OAuth provider. For example, if sign in and/or sign up with facebook functionality needs to be implemented, the developer needs to visit the official docs page for facebook OAuth provider.
Ability to handle non-web clients
In the OAuth2 authorization process, the program that sends requests to the authorization server is known as the client. The client can be a browser, a mobile app or any other device. That's how OAuth2 is able to handle non-web clients also.
How OAuth2 Works
Before discussing how OAuth2's working principle, it would be better if we discuss the key roles played by each component in this protocol.
-
Resource Owner: It refers to the user who gives permission to authorize an application in order to access their account. The authorization's scope determines the application's access to the user's account.
-
Resource or Authorization Server: The authorization server is responsible for verifying the identity of the user. Resource server refers to a server that hosts the protected user's accounts.
-
Client: It refers to the application that accesses the user's account. But, in order to do so, it must be authorized by the user, and that authorization process must go through a validation process carried by an API.
Now, you know the roles played by each component; let's discuss the overall workflow of OAuth2 in simple words.

-
The client or the application sends requests for authorization to access resources from the resource server.
-
If the user accepts the request, the application receives permission to access the user's data as per the scope of the permission.
-
The client requests an access token from the authorization server or API representing the authenticity of its own identity. These access tokens life span is very short, think of their life span in terms of hours and minutes.
-
If the authorization server authenticates the application's identity, then the server generates an access token to the application.
-
The application requests the resource from the resource server or API. Then it sends the access token to the server for authentication.
-
If the resource server finds that the access token is valid then it serves the resource to the application.
You need to register your application before using OAuth2 with it. It can be done by visiting the service's website's developer portion. The following details are required in order to do this.
-
Application Name
-
Application Website
-
Callback or redirect URL
What is Redirect URL in OAuth2
Redirect URL means where the service will redirect users after they authorize or deny your application. It also points to the route where you will write codes to handle access tokens.
What is Client Id in OAuth2
After registering the application, the service issues client credentials in the form of client id that is nothing but a unique string to identify the application and it is used by the service itself. Also, it helps to create an authorization URL that is displayed to the users.
What is Client Secret in OAuth2
The client secret's role is to authenticate the identity of the application to the service API when the application requests to access a user's account. The value of the client secret must be kept as a secret and should not be disclosed to anyone.
What is Refresh Token in OAuth2
We already discussed that the access token has a very short life-span. When the access token expires then refresh token enables the client to reauthorize without asking the resource owner to reauthenticate.
Alright, we discussed basics about what OAuth actually is, why we need it and what is the internal working principle behind OAuth2. Let's get down to building a node js application having facebook login built inside it that uses OAuth protocol.
Creating OAuth2 Facebook Application
At first, we need to create a facebook application, to do so visit the facebook developers page. Then log in with your Facebook account, this step is necessary because after doing this you will be able to get an application id and application secret that is mandatory for connecting our node js application with Facebook.
- After login click on the "Get Started" button, then you will something similar as shown in the screenshot below.

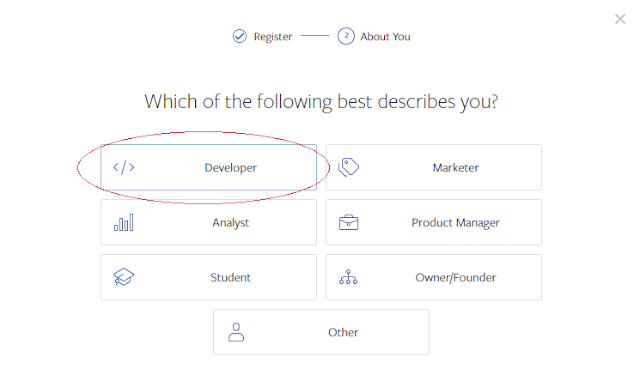
- Click on the "Next" button, then you need to choose your job role. Choose "Developer" (recommended).
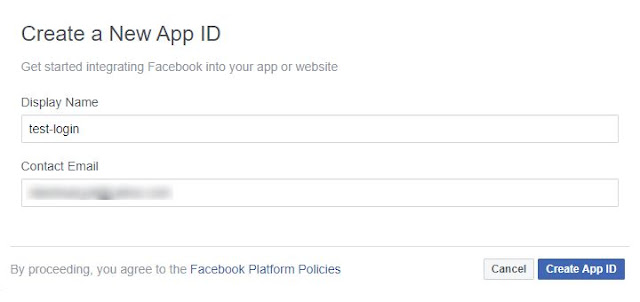
- You need to create an app first, the screen-shot for this step is shown below.
- Click on "I am not a robot" option checkbox.

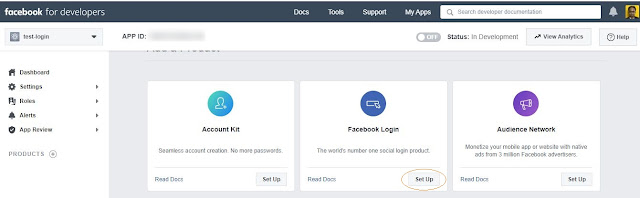
- After this step, you will be redirected to the "Add Product" page. On that page, click on the "Setup" button.
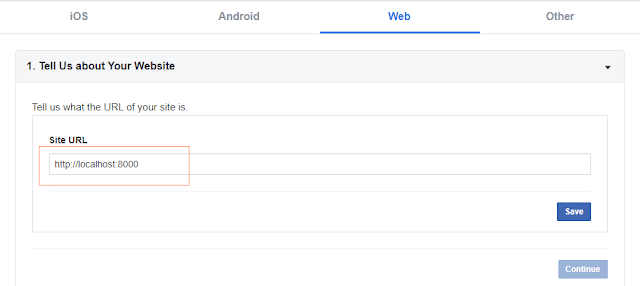
- Then you need to choose the platform for which you want to add facebook login functionality. Select "www" option.

- Then you need to enter the URL of your website. If you do not have a site in production, you can definitely use "localhost". I used "http://localhost:8000" for my this application. Click the "Save" button.
- Then skip the rest of the steps, click the "Settings" option in the left-hand menu.
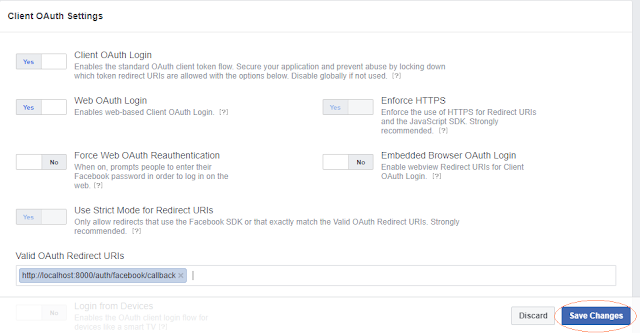
- In the Settings page, you need to add redirect URL in order to tell facebook where a user will be redirected back after authorization. Here, again I am using localhost for doing this. I have added "http://localhost:8000/auth/facebook/callback" as the redirect URL. Click on the "Save" Changes button.
- Then go to the main settings link in the top-left position. That is highlighted in the screen-shot shown below.
- You will see app id and app secret keys, copy these and paste them somewhere. We will need them later.
That's it, you have successfully created a facebook application which is the first step for integrating facebook login to the node js application that we will create.
Conclusion
I hope now you have a clear understanding of how oauth2 can be used to provide facebook login to a node js application. If you find this article helpful, consider sharing it with others. Thank you.