
Angular provides a lot of options to perform validations for the HTML form. To fulfill this need, we can use template-driven forms in angular. This article will walk you through each and every detail regarding the template-driven form validation approach in angular.
Let's start talking about what actually is angular forms first, then we will dive deeper into template-driven form.
Why Angular Forms?
Generally, in every frontend applications, forms play an important and inevitable part. This statement is especially true for huge, enterprise-grade applications. Sometimes, users need to fill out a form that consists of multiple tabs.
To solve this need to handle forms properly, angular provides powerful tools; angular forms. That comes as a built-in feature when we build any angular application from scratch. We don't need to rely on third-party packages to work with angular forms.
So if anything goes wrong while the user fills out the form, they must be notified what is the reason that causes that problem. To tackle that situation angular itself provides two approaches.
- Template Driven Forms
- Reactive Forms
What is Template Driven Form in Angular?
You can think of a template-driven form similar to an HTML form. The only difference is that in this type of form, we need to use angular specific directives, events, etc. In this approach, we define the actual template that we want to use in forms. That's why this approach is called a template-driven approach.
In other words, you can say that in the template-driven form we write our logic, validations, etc. in the template part ( i.e, HTML code). Template-driven forms are named primarily because the form controls are defined in the template of the component.
As the form is primarily defined in the template layer, it also means that the validation errors are managed through the template.
Before we jump into how you can actually work with template-driven forms, it would be better if you know how template-driven forms actually work behind the scene.
Template Driven Forms: How They Actually Work?
To clearly understand the actual inner-working principle behind template-driven forms first, you need to be familiar with two terms which are as follows.
-
FormControl
-
FormGroup
What is FormControl in Angular?
As per angular's official docs: FormControl tracks the value and validation status of an individual form control.
After reading the description about form control from the official site, you may feel confused and thinking of what actually is form control. Let me explain what is form control.
Basically, FormControl is a class that inherits the AbstractControl class in angular. This class can perform various tasks, such as accessing the value, act according to how the user interacts with the form, respond as per the events occurred while the user fills in the form, etc.
So, for each input field in our form, we need to create an instance of the FormControl class. With the help of this class, we can check different things.
For example, we can get the value of the input field, we can check if the content of input field has been changed or not, we are also able to check if the field contains a valid value or not.
If we found that the field doesn't have valid values, we can display validation errors for that particular field.
There exist different properties in FormControl. These are as follows.
-
valid
-
invalid
-
dirty
-
pristine
-
touched
-
untouched
-
value
-
errors
What is dirty in the Angular Form?
Simply saying, by the term "dirty", angular is able to detect that the field's content has been changed by the user.
What is Pristine in Angular?
In simple words, "pristine" tells angular that the field's content has not been modified by the user.
Ok, then tell me about touched and untouched
At a glance, you may think that the term "touched" means that the user has not touched the form-field. Yeah, you are right!
In terms of programming, "touched" means that the user has placed the focus on that particular field. By the term "focus" I mean the user puts the cursor blinking in that field so that he or she can start typing content there.
I guess I don't have to discuss what "untouched" means.
Let's talk about the angular form's error object
In one sentence, all the errors that result after the user fill out the form are stored in the error object. These errors are stored in form of key-value pairs. In which the field name itself is the key and the error message is the value for that corresponding key.
What is Form Group in Angular?
According to angular's official website: FormGroup tracks the value and validity state of a group of FormControl instances.
Let's discuss what is form group and its purpose. FormGroup is a class that represents a group of controls in a form. Each of the forms refers to a form group.
Technically we can say that each form group can consist of multiple form control elements in angular. As we know earlier, we can easily access each form control elements various properties (e.g, valid, invalid, dirty, pristine, etc.).
Template Driven Forms: A Simple Example
Let's assume we want to build a checkout form for an e-commerce store that takes the user's first name, last name, address, etc. under the Billing Info section. Then in Payment Info section user enters details such as the name on the debit card, card number, expiry date, CVV number, etc.
Please note that angular material is used to build the user interface of this application. If you don't know about it, you can check out this article here.
Following is the screenshot of the app.

Explanation of app.component.html File
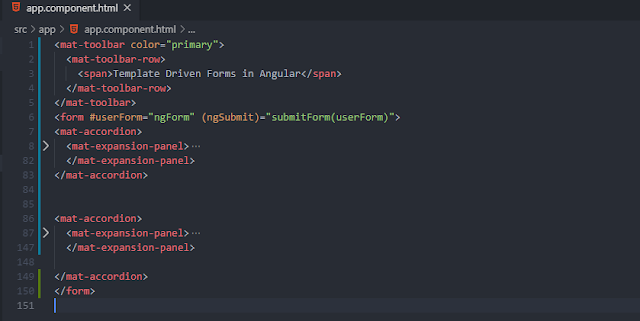
In the above code snippet of the app.component.html file, we have created two expansion panels. The main purpose of it is to represent similar form elements together as a single entity. First of the panel will hold all billing information, while the second one will hold all details regarding the payment information that the user will provide to make the payment.
We also applied a directive called "ngForm" that is provided by angular automatically. Its main purpose is to keep track of the form's overall validation status. But, under the hood, it creates a FormGroup instance at the top level.
We want to properly handle the validation for each individual form elements. To achieve this, we have created a template variable "userForm" and assigned ngForm to that variable. After doing that, we are able to get values for properties like dirty, touched, pristine, etc.
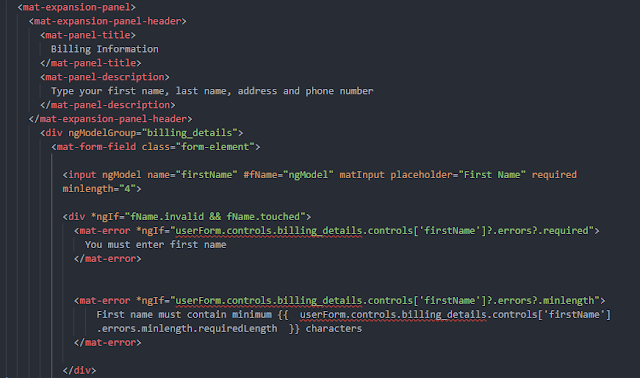
Here, we have applied a "ngModel" directive to the input field that asks user to enter his or her first name. In template driven approach, angular will create a FormControl object and associate the input field with that object.
Also, we must set name property for that input field, it is mandatory to do so. Otherwise, angular will not be able to distinguish that input field.
Later, we want to make sure that if user did not fill up the first name, the user will be notified that he or she forgot to do so. For this purpose, we have created a local reference variable called "fName" and stored "ngModel" in that variable.
We are using HTML5's built-in "required" validator. Then with the help of ngIf directive, we check to see if first name field has focus and it is invalid. If these conditions are true we set the show user a message "You must enter first name".
With the help of
Now, you may wonder why "ngModelGroup" directive is used. Let's explain the main role of it. Sometimes, we may need to send a complex object to the back-end after submitting the form. For this purpose, angular make use of this directive.
For example, in this example, we want to send billing information as well as payment information to the back-end. Under billing, we have fields such as first name, last name, gender, etc. Inside payment, we have card number, CVV number, etc.
So, it logically makes sense to send billing data inside the "billing_information" object and payment data inside the "payment_information" object. That's why, we created two div elements and assigned first ngModelGroup's value "billing_information" and second value as "payment_information".
Explanation of app.component.ts File
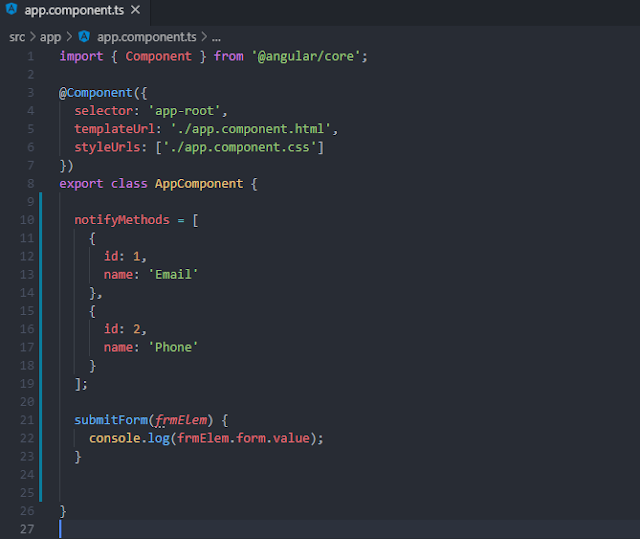
Here, we are handling the "ngSubmit" event emitted by the "ngForm" directive. We simply wrote the code to display the submitted data in the browser's console window.
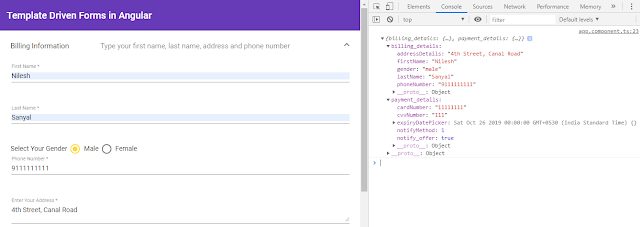
The screen-shot of the submitted data is shown below.
Final Words
I hope that after reading this article on angular template-driven forms, you have a clear concept in it. If you have any doubts, you can ask me questions. If anyhow this article proves beneficial to you, please share it among others. Thank you!